목차
-booting과 /etc/rc
-login과 /etc/passwd(shadow)
-networking과 여러 가지 file
-/etc/hosts, /etc/services, /etc/protocols
-/etc/networks
booting과 /etc/rc
- Booting : 컴퓨터가 처음에 power on을 하거나 reset을 했을 때 처음 시작되는 프로그램.
bootstraper -> Boot Block(disk에 있음) -> OS
이 과정의 마지막에서 /etc/init(pid=1을 생성하는 process) 이 불려옴 ->다른 process는 전부 init의 fork()
-init process : 시스템 초기화를 함. 처음에는 single user mode로 수행.
shell program fork, stdio descriptor, system console terminal 생성. (하는 일이 많구만)
-multi user operation
이 과정에서 일어나는 자세한 일 : shell을 만든다->/etc/rc에 있는 interpret하여 수행시킴
/etc/rc : 시스템 초기화에서 수행해야 하는 일이 있음
+파일 시스템 체크, cron, syslog 데몬 생성, /etc/mtab file 작업 가능
terminal device에 관련된 cofiguration file(/etc/tty)을 읽어서 한 entry마다 사용자 접속을 감지할 수 있는 프로그램(/etc/getty) 생성
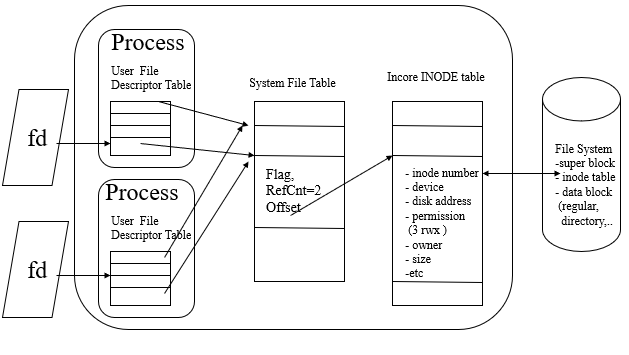
init이 불려올 때의 위 과정들을 정리하자면 다음 그림과 같다.

login과 /etc/passwd(shadow) System Data File
-passwd
passwd 파일에 있는 예시를 가져와서 각 요소가 뭘 의미하는지 살펴보자. 분리자는 :이다.
예시만 보면 답답하니까, 직접 shell 창을 켜서 찾아보자 passwd는 /etc에 있다.
cat passwd를 하면 목록이 쭉 뜬다. root를 일단 살펴보자.

user name : encrypted password : numerical user id : numerical group id : comment field : initial working directory(home directory) : initial shell(user program, 사용하는 shell.)
의 순서대로 이루어져 있다. (볼 수 있는 세상이 넓어졌다!)
-passwd 관련 system call
[간단상식 ] get - return / set - write
| struct passwd *getpwuid(uid_t uid) | uid를 통해 passwd를 얻겠다! |
| struct passwd *getpwname(const char *name) | name을 통해 passwd를 얻겠다! |
passwd struct는 다음과 같은 요소들이 들어있다 ...
– char *pw_name
– char *pw_passwd
– uid_t pw_uid
– gid_t pw_gid
– char *pw_gecos
– char *pw_dir
– char *pw_shell
-home directory(~)
시작했을 때, 사용자마다 home directory에 login 정보가 들어있는 system data file이 있다.
+login
/bin/sh
~/.profile : (.login + .cshrc)
/bin/csh
~/.login : set terminal type, environment vars(fork, exec 할 때 e 변수에 관련된 것)
~/.cshrc : set command alias, path, umask(access control에 해당. umask에서 masking 되어있으면 해당하는 access permission이 protection함. default mask값 설정)
+logout
/bin/csh
~/.logout : logout할 때 해야 하는 동작들.
networking과 여러 가지 file
-Login Procedure(로그인 과정)
+terminal login

+network login

우리는 알고 있다. 이 그림들을 다시 자세히 보게 될 것이라는 것을 ... 그냥 통짜로 정리해보자.

-/etc/hosts, /etc/services, /etc/protocols
+/etc/hosts : 각 host에 대한 정보. ip주소, hostname가 기록되어 있는 system daa file
+/etc/service : IP + port(service, 프로세스 관련)
+/etc/protocol : transport layer에서 어떤 protocol을 사용하는지 (TCP, UDP)
위의 정보들을 총정리한 표 역시 존재한다!

'SSS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| SSS-3. UNIX 시스템 호출 (0) | 2020.04.12 |
|---|---|
| SSS-1_2. UNIX 시스템 소개 및 구조 (2) | 2020.04.11 |